Development of sustainable, biodegradable and compostable nonwovens
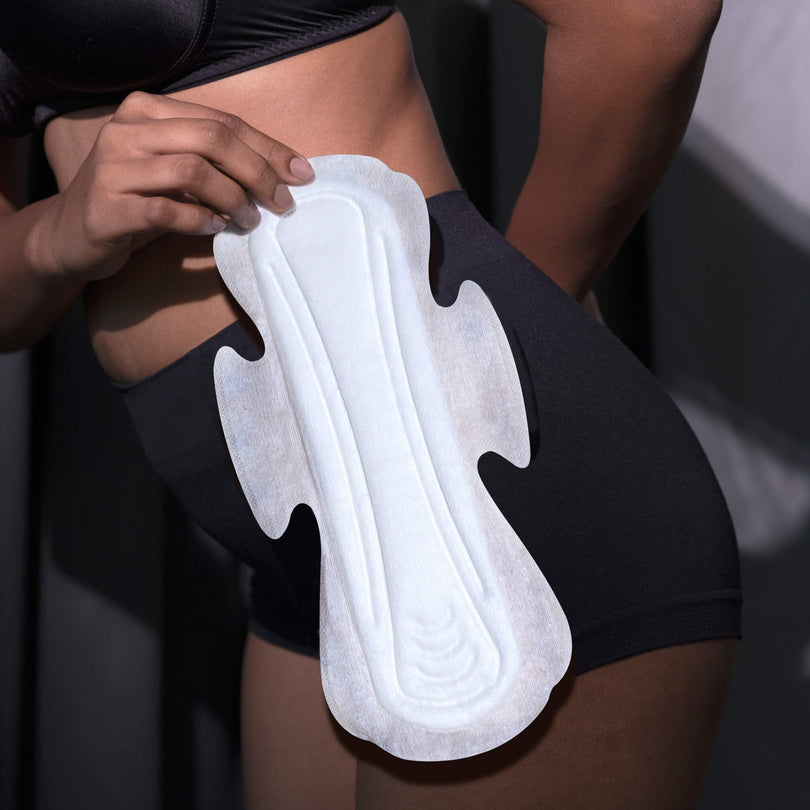
Made from soft fibers, nonwoven fabrics are typically used as the top sheets of absorbent hygiene products. In conventional sanitary pads, the top sheet is made from polypropylene (PP) or perforated polyethylene (PE), both of which are non-biodegradable and are by-products derived from petrochemicals.
Our Nonwovens department is centred around utilizing renewable resources to make sustainable products that can also biodegrade without leaving any microplastics or toxic residue behind. We focus on utilizing natural cellulosic fibers such as jute, banana fiber, sisal, hemp, flax, etc that can offer a sustainable alternative to conventional, synthetic, non-biodegradable fibers. Our research areas at the present include:
1. 100% plant-based, natural cellulose fibers for making nonwovens
2. Sustainable regenerated cellulose derived from non-wood fibers

100% plant-based, natural cellulose fibers for making nonwovens
At our Nonwovens lab, we are conducting research on developing fiber processing technology to transform raw natural fibers such as banana fiber, jute fibers, hemp and flax to produce sustainable, tree-free and plastic-free nonwoven fabrics suitable for absorbent hygiene products. By replacing synthetic and non-biodegradable fibers that follow traditional 'take-make-waste' linear economy, we are focusing on utilizing renewable resources and using natural, biodegradable and compostable fibers that support a circular economy.
To obtain clean, bright, and intact natural cellulose fibers, we eliminate the non-cellulosic parts of the plant such as lignins, gums, pectins, and hemicellulose through a series of environmentally-responsible processes and treatments.
100% plant-based, natural cellulose fibers for making nonwovens
At our Nonwovens lab, we are conducting research on developing fiber processing technology to transform raw natural fibers such as banana fiber, jute fibers, hemp and flax to produce sustainable, tree-free and plastic-free nonwoven fabrics suitable for absorbent hygiene products. By replacing synthetic and non-biodegradable fibers that follow traditional 'take-make-waste' linear economy, we are focusing on utilizing renewable resources and using natural, biodegradable and compostable fibers that support a circular economy.
To obtain clean, bright, and intact natural cellulose fibers, we eliminate the non-cellulosic parts of the plant such as lignins, gums, pectins, and hemicellulose through a series of environmentally-responsible processes and treatments that include fiber extraction, decorticating, degumming (chemical, microbial, and enzyme process), mechanical cleaning, fiber softening, carding, and combing, while maintaining the fiber length, diameter, brightness and overall fiber integrity. In order to enhance softness and to make the fibers suitable for specific tailormade applications, we apply additional treatments to individual fibers or small fiber bundles so that single cellulosic strands can get separated and be freed from the fiber matrix.

Sustainable regenerated cellulose derived from non-wood fibers
Along with developing fiber processing technology to transform 100% natural fibers into hygiene-grade nonwovens, we are also conducting research on utilizing agro-based, renewable plant fibers such as bamboo, bagasse (sugarcane fiber), jute and hemp fibers to develop regenerated cellulose via an environmentally-friendly, sustainable, low energy, low water, closed-loop system which can recycle almost all the chemicals used in production.
As an alternative source of fiber to conventional. non-biodegradable, synthetic fibers, environmentally responsibly produced regenerated cellulose can act as a sustainable, biodegradable and compostable alternative.
Sustainable regenerated cellulose derived from non-wood fibers
Along with developing fiber processing technology to transform 100% natural fibers into hygiene grade nonwovens, we are also conducting research on utilizing agro-based renewable plant fibers such as bamboo, bagasse (sugarcane fiber), jute and hemp fibers to develop regenerated cellulose via an environmentally-friendly, sustainable, low energy, low water, closed-loop system which can recycle almost all the chemicals used in production.
As an alternative source of fiber to conventional, non-biodegradable, synthetic fibers, environmentally responsibly produced regenerated cellulose can act as a sustainable, biodegradable and compostable alternative. As regenerated cellulose can be made of nanofibrils, it can offer superior wicking and absorption properties which can be ideal for sensitive skin.